As an Amazon affiliate, I may earn from qualifying purchases. Please read our Disclaimer and Privacy Policy.
This post is related to pregnancy at 43 statistics. Specifically, however, it’s aimed at anyone aged 40 and over who is either planning a first baby, or is already pregnant.
You’re going to read a lot of risks that you’ll find on most websites dedicated to women’s fertility. Don’t be too alarmed! The facts are the facts, but there are always exceptions. These days, fertility treatments and prenatal care have come a long way.
In fact, according to the National Center for Health Statistics, the number of live births among women aged 40-44 has increased significantly in recent years.
The success rates of assisted reproductive technology (ART), particularly IVF, have also improved, offering hope to many women in this age range.

My mother gave birth to me when she was 40
In 1967, my mother was faced with an unplanned pregnancy at 40 years old.
After not getting pregnant 16 years after her last child, she assumed she couldn’t get pregnant. Like many women, she thought the symptoms she was experiencing had to do with the “change of life”.
The symptoms of pregnancy and perimenopause can be similar. Missed periods, fatigue, sore breasts, mood changes, etc. So, my mother assumed she was going through the “change”, as she called it.
Just to be sure, she went to her doctor and was floored to discover that, at 40-years-old, she was pregnant with me.
Are you experiencing an unplanned pregnancy in your 40’s?
Pregnancy over 40 has become more common, thanks to advances in reproductive medicine and fertility treatments.
While this age group faces unique challenges, many older women are successfully having healthy pregnancies and healthy babies.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the statistics and factors that affect pregnant women over 40, using data and insights from leading health organizations.
I’ve also added my sources at the bottom of this post.
Disclaimer
The information presented in this blog post is based on the latest statistics and data from reputable sources, which are listed at the bottom of this article.
However, please note that statistics and medical guidelines may have changed since the time of writing.
This content is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider, such as a pediatric physician or fertility specialist, to discuss your specific circumstances and any potential risks.
The information presented in this blog post is not designed to take the place of medical advice.
Facing the Unexpected: What to Do If You’re Pregnant Over 40
Discovering that you’re pregnant over 40 can bring a mix of emotions. Of course, it’s important to focus on your health and well-being as you navigate this new chapter.
Did you know that women in their 40s are considered to be of “advanced maternal age”? It’s a term used to describe pregnancies that carry a higher risk of complications. You may have even heard it called a “geriatric pregnancy”.
If you’rke over 40 and expecting, it’s vital to schedule a visit with a physician as soon as possible. Once your pregnancy has been confirmed with a blood test, the doctor may arrange or suggest the following:
Prenatal Vitamins
Prenatal vitamins, especially folic acid, are important in eary pregnancy to help reduce the risk of birth defects. Your medical practitioner will let you know how much to take.
Review Health History and Risk Factors
Early prenatal care is crucial for monitoring both maternal health and the baby’s development. Your doctor may recommend blood tests and ultrasounds to detect any issues early on.
Genetic screenings are often advised for pregnancies in this age group to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome.
The doctor will perform a blood test to confirm the pregnancy. An ultrasound should be performed to check for viability and rule out complications like an ectopic pregnancy.
Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle
Now is a great time to start eating a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, if you haven’t already. It’s important to continue or start a moderate exercise routine and avoid alcohol, smoking, and limit caffeine intake.
Special Precautions
Pregnancy in women over 40 is considered higher risk, so additional monitoring and preventive measures are often necessary.
These could include the following:
- More frequent prenatal visits
- Comprehensive screening for genetic conditions
- Monitoring for gestational diabetes and hypertension
- More frequent ultrasounds to monitor fetal growth
- Increased monitoring for placenta-related issues
- Management of pre-existing conditions
- Close monitoring of weight gain
- Consideration for early delivery because women over 40 are more likely to experience complications.

Are you trying to become pregnant over 40?
Trying to conceive after 40 may not be easy. The reality is that a women (from puberty to the time she turns 20) has anywhere from 300,000 to 500,000 eggs. As a woman ages, there is a gradual decline of healthy, viable eggs available.
Fast Fact:
One in four people in their 20’s and 30’s will get pregnant in any one menstrual cycle whereas only 1 in 10 women in their 40’s will get pregnant in any one menstrual cycle.
Considerations When Trying to Get Pregnant Over 40
As women age, fertility rates naturally decline.
By the time a woman reaches her late 20s, her ovarian reserve— the number of viable eggs she has—begins to decrease.
This decline becomes more pronounced in the early 30s and continues sharply after 35. For women over 40, this can mean a lower chance of pregnancy using their own eggs.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), have significantly improved the chances of conception.
IVF treatment often involves the use of donor eggs, especially for older women with diminished ovarian reserve. This can increase the chance of a successful pregnancy.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, IVF success rates using donor eggs (from a younger woman) are higher compared to using a woman’s own eggs at an older age.
Be Proactive
It’s important to be proactive in understanding your fertility health and working with specialists.
One of the first steps is to schedule a consultation with a fertility specialist. The specialist can offer fertility assessments and guide you through potential treatments, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or egg retrieval.
These procedures can significantly improve your chances of pregnancy.
In addition to fertility treatments, your specialist will likely evaluate you for any chronic conditions, like high blood pressure or diabetes, which could impact both your fertility and the health of a future pregnancy.
Making lifestyle changes, such as improving your diet, managing stress, and quitting smoking, can also increase your chances of conceiving.
It’s essential to be informed about the increased risk of complications, such as preterm birth or maternal health concerns, and work closely with healthcare professionals to navigate your fertility journey safely.
Health Risks and Complications For Pregnant Women Over 40
Pregnant women over 40 face higher risks of complications. These include:
Gestational Diabetes and High Blood Pressure
Pregnant women over 50 have an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes and hypertension.
These conditions require careful monitoring and management by a health care provider to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Chromosomal Abnormalities
The risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, rises with maternal age. Genetic tests, including blood tests and chorionic villus sampling, can help detect these issues early in pregnancy.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication causing high blood pressure and damage to organs like the liver and kidneys.
It usually develops after 20 weeks of pregnancy and can affect both the mother and the baby.
Preeclampsia can be dangerous if left untreated, potentially leading to life-threatening complications such as eclampsia (seizures) and preterm birth.
Women under 20 and over 35 are at increased risk. In addition, preeclampsia can occur postpartum or after delivery.
Preterm Birth
Pregnant women over 40 are at a higher risk of a preterm birth. This refers to deliverying a baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
A preterm birth can occur if there are problems with the placenta, if the mother has chronic health conditions, cervical insufficiency, multiple embryo transfers during IVF treatments, infections, inflammation, or abnormal levels of amniotic fluid.
In some cases, a perterm birth is medically induced due to concerns about the health of the mother or baby.
Need for a Cesarean Section
Pregnant women over 40 have a higher likelihood of requiring a c-section for a number of reasongs. For example:
- They are at an increased risk of pregnancy complications
- The women may develop placenta problems
- Women over 40 are at a higher rate of having twins or multiples
- There may be a prolonged labor
- Fetal distress can necessitate a c-section
- Breech baby or abnormal fetal position
- Increased risk of large babies where the baby could get stuck during delivery
- Some women over 40 may elect for a c-section to avoid common problems associated with delivery
Greater Chance of Miscarriage
Pregnant women over 40 face a greater risk of miscarriage due to age-related declines in egg quality and an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Lower IVF Success Rate
Women over 40 who are trying to get pregnant have about a 5% chance of pregnancy per intrauterine insemination cycle. Overall, the success rate per in vitro fertilization (IVF) is less than 20%.
Risk of Maternal Death
The risk of maternal death, while still low, is higher for older women.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that maternal mortality rates are highest among women aged 40 and older. This is why comprehensive prenatal care is so important to reduce the risks to the mother and her baby.
It’s Not All Bad News!
Despite these risks, many women over 40 deliver healthy babies. This is usually because the woman is in good health and has access to quality prenatal care.
Many women in their 40’s also tend to be emotionally and financially ready for a baby.
IVF Advancements
There have been great advancements in fertility treatments such as IVF in the past years. In fact, many women over 40 successfully conceive and carry healthy pregnancies.
Increased Births Among Women Over 40
In the United States, the average age of first births has been rising.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, the number of live births among women aged 40-44 has increased significantly in recent years. The success rates of ART, particularly IVF, have also improved, offering hope to many women in this age range.

Pregnancy at 43 Statistics
The following statistics were taken from a number of resources. The sources are listed at the bottom of this post in no particular order.
Please keep in mind that statistics can be a moving target and tend to change as things evolve over time.
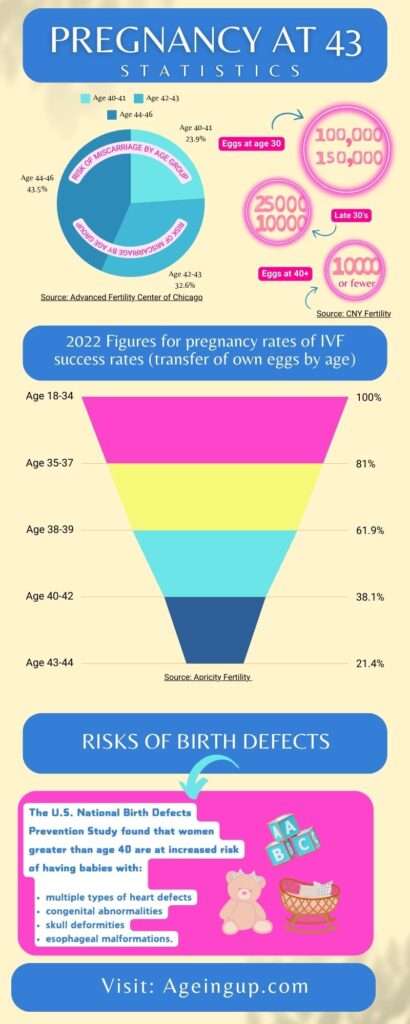
| 1 in 4 people in their 20’s and 30’s will get pregnant in any one menstrual cycle, whereas only 1 in 10 women in their 40’s will get pregnant in any one menstrual cycle |
| At age 40 you have a 44% change of becoming pregnant naturally in any 1 year |
| By the age of 37, women are down to approx 25,000 eggs compared to puberty when there are approximately 300,000-500,000 eggs |
| At age 40, 27% of pregnancies end in miscarriage |
| Birth rates in women aged 40-44 have increased since the 1990’s |
| The risk of having a baby with Down syndrome at age 40 is 1 in 85 |
| The risk of having a baby with Down syndrome at age 45 is 1 in 35 |
| Pregnant women over 40 have an increased risk of delivering their babies preterm |
| Women over 50 have a 50% chance of requiring a c-section |
| IVF success rates fall significantly when women use their own eggs after 35 |
| Nearly 4% of new babies are born to women age 40 and older |
| After age 35, the risk of ectopic pregnancy is as high as 4 – 8 times that of younger women |
| The U.S. National Birth Defects Prevention Study found that women greater than age 40 are at increased risk of having babies with multiple types of heart defects, congenital abnormalities, skull deformities, and esophageal malformations. |
| The success rate for IVF for women 40-42 (using a woman’s own eggs) is about 5-12% per cycle. |
| The success rate for IVF for women aged 43 and above drops to about 1-5% per cycle. |
Conclusion
Pregnancy over 40 comes with its share of challenges, but with the right care and support, many women can achieve a successful pregnancy and deliver healthy babies.
If you’re considering pregnancy at an older age, consult with a fertility specialist to understand your options and get personalized medical advice. Staying informed and proactive is key to navigating this exciting journey.
For more information, you can refer to resources from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the CDC, and other reputable health organizations.
Sources:
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2023). Age and Fertility: A Guide for Patients.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Maternal Mortality Rates.
- National Center for Health Statistics. (2023). Birth Data.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2023). Obstetric Care Consensus.
- webmd.com/baby/pregnant-at-40
- Medicalnewtoday.com
- Virginia Physicians for Women

